
 |  |  |
| | Home | World of Noh | Masks |
 Masks
Masks
| Other Roles | Stage | Noh Masks | Props | Vocal | Music | Noh Dance | Movement Patterns |
| Costumes | What is Kyōgen |

As Noh is an art form that utilizes masks, there is a great variety of them. There were originally about 60 basic types of noh masks, but today there are well over 200 different kinds in use.
Covering the face with a mask is much like wearing makeup. However, noh performers feel that the noh mask has a certain power inherent in it which makes it much more spiritual than a prop used to change ones appearance. Taking into account the status of a certain noh, the noh performer will carefully choose a noh mask, known also as a noh-men or omote. In most cases, the exact mask is not predetermined, but depending on which noh is being done, the shite has a variety to choose from. In the end, it is up to the shite to make the final determination as to which mask is chosen.
Origin of the Noh Mask
Exactly when the noh mask came into being is not entirely clear however it is believed that masks, and their names still used today, were developed from the mid to latter part of the Muromachi period (1392-1573). Previous to that time, the mask conventions were not entirely set and masks themselves had stronger religious connotations. It was during the Muromachi period that the religious significance of the masks began to wane and they took on more human characteristics. It is thought that as performers started to think more about the use of yūgen (mysterious beauty) and profundity, they felt they needed to hide the unattractive aspects of their own faces and concentrate on making the beauty of noh stronger.
Between the end of the Muromachi period and the modern age the art of making noh masks was established as a hereditary art with a long lineage. Two examples are the Deme family from Echizen (present day Fukui prefecture) and the Iseki family from Ohmi (present day Shiga prefecture). Following the establishment of noh mask making families, the stylization of noh masks significantly advanced. Even today there are many independent mask makers. While some nohgaku performers still make their own masks, the performance world and the mask-making world are essentially independent of each other.
Noh Mask Expression: Teru and Kumoru
As it is often difficult to tell the actual feelings expressed in a noh mask, it is said to be made with a “neutral” expression. The mask carver tries to instill a variety of emotions in the mask.
It is up to the performer to imbue the mask with emotion. One of the techniques used in this task is to slightly tilt the mask up or down. With terasu (tilting upwards) the mask appears to be slightly smiling or laughing and the expression lightens somewhat. While kumorasu (tilting downwards), produces a slight frown and can express sadness or crying. Basically, by using minute movements, the performer is able to express very fully.
Putting on a Mask

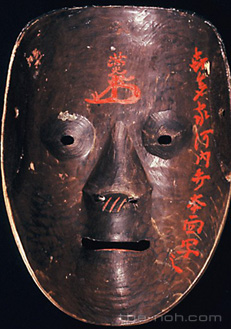
Noh masks, like costumes and props, are extremely valuable heirlooms and handed down from generation to generation.
After having the costume put on, the shite then goes to the kagami no ma (mirror room) where in front of a mirror, the shite faces the mask. In putting the mask on, the word kaburu (putting on clothing) is not used. Instead the word kakeru (to hang) or tsukeru (to attach) is used. In this way, it is implying that the performer is “becoming” the mask, and its emotions, in order to better express the characters feelings.
In reality, a noh mask does not entirely cover a noh performer’s face when it is being worn. In fact, it is thought best if some part of the chin and/or jowls show.
Also, as the eye holes of the mask are very small, the field of vision of the performer is very limited when wearing the mask. Consequently the simple design of the stage and the use of hashira (pillars) assists in helping the performer know their location during a performance.
Hitamen
Not all the main performers on stage wear masks in noh. Usually the shite and the tsure wear masks and occasionally there are instances where the ai will as well. The waki as a rule, playing a character who is living in the present, does not wear a mask. This is called hitamen or a “direct mask.”
However, even without wearing a mask, the performer is meant to “make their face a mask.” The performer must inject power and emotion into their performance while not using their face to express. In some genzai noh the shite or tsure do not wear masks.
Types of Noh Masks
- Okina (Old man masks)
- This type of mask originated from sarugaku, the predecessor of noh, in the latter part of the Heian period. This is the oldest type of noh mask.
- Jō (Elders masks)
- Examples of this type are the Kojō, Asakurajō, Sankōjō and Waraijō masks. These masks are often used in the first half of first or second category noh when the shite is portraying a spirit.
- Onna-men (Woman masks)
- When most people think of noh these are the masks that come to mind. That being the case, these tend to be the most varied and popular masks. These masks are categorized by age and character.
Examples of beautiful young women masks are the: ko-omote, wakaonna, zō and magojirō. The ōmiona mask also portrays a young woman, but with more of a working class background. Fukai and shakumi masks are both used to play mature, middle-aged woman of elegance and grace however the latter displays a stronger character. The deigan mask has gold rimmed eyes which implies that the character is otherworldly. Examples of masks for playing old women are rōjo and uba. - Otoko-men (Man masks)
- Heida, chūjō, jūroku, hatachi-amari, dōji, kasshiki, and yase-otoko are all examples of masks in this category which are classified according to social class and character.
- Kishin (Demons)
- These masks were developed early in noh’s history and are used for portraying demons, goblins or other worldly creatures. This category is divided into two main parts, tobide (fierce gods or demonic spirits) and beshimi (goblins and other creatures).
- Onryō (Ghosts and Spirits)
- These masks are used for spirits of the dead who have regrets of some kind. In this category there are both male and female masks. Examples of male types are ayakashi, yase-otoko and kawazu. Examples of female types are yamamba, deigan and the famous hannya masks.
![]() For more on noh masks, including pictures and summaries, please go to the Noh Mask Database
For more on noh masks, including pictures and summaries, please go to the Noh Mask Database